Gray Zone Challenge: Intent And Military Response
Gray Zone Challenge: Intent And Military Response.
Author | Editor: Elder, R. (USAF, ret) & Levis, A. (George Mason University).
Abstract
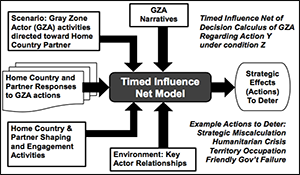
Mapping political, security, societal and economic trends to the decision calculus of key regional and (as applicable) non-state actors has been used to gain insights into the behaviors of actors conducting multi- instrument operations in the “gray zone” between peace and conflict. Timed Influence Net (TIN) models have been used to identify potential sources of strategic risk, and serve as the foundation for a planning framework designed for use by operational planning teams to support operational and engagement planning by Combatant Commands and their components. Computational experiments were performed using the TIN models. The computational experiments focused on gray zone actor perceptions of the decision calculus to counter the effects of gray zone activities.

Comments