m-Best 2-D Assignment Algorithm Parallelization
Dynamically Adaptable m-Best 2-D Assignment Algorithm and Multilevel Parallelization
Author: Popp, R., Pattipati, K. & Bar-Shalom, Y.
Abstract
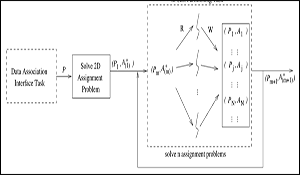
In recent years, there has been considerable interest within the tracking community in an approach to data association based on the m-best two-dimensional (2-D) assignment algorithm. Much of the interest has been spurred by its ability to provide various efficient data association solutions, including joint probabilistic data association (JPDA) and multiple hypothesis tracking (MHT). The focus of this work is to describe several recent improvements to the m-best 2-D assignment algorithm. One improvement is to utilize a nonintrusive 2-D assignment algorithm switching mechanism, based on a problem sparsity threshold. Dynamic switching between two different 2-D assignment algorithms, highly suited for sparse and dense problems, respectively, enables more efficient solutions to the numerous 2-D assignment problems generated in the m-best 2-D assignment framework. Another improvement is to utilize a multilevel parallelization enabling many independent and highly parallelizable tasks to be executed concurrently, including 1) solving the multiple 2-D assignment problems via a parallelization of the m-best partitioning task, and 2) calculating the numerous gating tests, state estimates, covariance calculations, and likelihood function evaluations (used as cost coefficients in the 2-D assignment problem) via a parallelization of the data association interface task. Using both simulated data and an air traffic surveillance (ATS) problem based on data from two Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) air traffic control radars, we demonstrate that efficient solutions to the data association problem are obtainable using our improvements in the m-best 2-D assignment algorithm.
Conclusion
Spurred on by recent interest in the m-best 2-D assignment algorithm for the data association problem, in this paper we described several improvements that enable much more efficient solutions to the data association problem, especially in dynamic environments. One improvement was to utilize a nonintrusive 2-D assignment algorithm switching mechanism, based on a problem sparsity threshold, enabling the auction and JVC 2-D assignment algorithms, each highly suited for sparse and dense problems, respectively, to efficiently solve the numerous 2-D assignment problems generated as part of the partitioning task. Another improvement was to utilize a multilevel parallelization of the data association problem, i.e., we parallelized the partitioning task and the data association interface task. This parallelization enables not only multiple 2-D assignment problems to be executed in parallel, but also the numerous gating tests, state estimates, covariance calculations, and likelihood function evaluations (used as cost coefficients in the 2-D assignment problem). Finally, using both simulated data and an ATS problem based on two FAA air traffic control radars, we demonstrated that more efficient solutions to the data association problem are possible when using the m-best 2-D assignment algorithm with our improvements incorporated.
Citation
Popp, R., K. Pattipati and Y. Bar-Shalom, “Dynamically Adaptable m-Best 2D Assignment Algorithm and Multi-Level Parallelization,” IEEE Trans. Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 1145–1160, Oct 1999.

Comments